Flora and Fauna of Ritsa relic national park
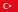
Up to a height of 1800-1900 m mountains Park of Ritsa, excluding the rocks are covered by continuous forest. In the lower zone - broadleaved forest Colchis, their main forest-forming species: Iberian oak, hornbeam, Caucasian, sweet chestnut, beech, eastern, southern framework, elm and maple species. Solitary meet yew, lime Caucasian, etc. Of particular note is the endemic forest of oaks, as well as a small part of the forest of arbutus and pine. Above 700 m in the mountain forests of the eastern area is dominated by beech and then increasingly appears Caucasian fir, sometimes completely replacing it. Light dominates the slopes of pine Koch, sometimes forming groves, rare for Colchis. For all of the forest zone is characterized by evergreen undergrowth of relics - Colchis boxwood, Holly Colchis, Pontic rhododendron, ivy Colchis and others.

The limestone canyons of the rivers in the rock crevices grow quite unique endemic species - the queen of the Abkhazian flora bell amazing (Al'bova), bell Kolakowski, Annaeus yastrebinovaya, bloodroot Camilla, aster Abkhaz, thoroughwax Abkhaz, Abkhaz gorse, columbine Gegsky and others.
One of the most valuable species of the Caucasus is the boxwood Colchis. Evergreen tree with small but lush foliage. It blooms in early spring, the fruits ripen in summer and in dry weather with a bang disclosed. The trunk and branches of boxwood covered with moss, which protects the wood from moisture loss during rapid temperature changes. It grows slowly - in year 1 mm in diameter. Wood yellowish, hard, sinking in water. Since ancient times, from Abkhazia to all countries exported raw materials from the tree. It is alleged that many of the Notre Dame Cathedral is made of boxwood Colchis. In the 30s of the 20th century industrial cutting boxwood banned, and later brought in the Red Book.
Yew belongs to the conifers, but does not contain the resin. Wood it is poisonous, so do not rot and pest damage, after soaking in lime water acquires a brown color. Living yews to 3000 years old, it is called red tree Caucasian. This conifer is listed in the Red Book. Yew can also be found in the Carpathians, the Crimea and the Baltic States.

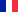
The fauna of the forest belt is also represented by a number of endemic Caucasian forms, many of which are rare in the entire range. Most rich in species composition and abundance of avifauna. Birds in Abkhazia - the largest group - of 273 species, of which 72 - are rare. In Ritsa park more than 130 species of birds, 94 of which nest in the Park, and the rest - span. Through the territory of the national park passes Eastern Black Sea migration route more than a hundred species of birds. It is home to the Caucasian chaffinch, blackbird, great tit, tit. In the dark coniferous forests of fir black-nest, Goldcrest, common crossbill, bullfinch, and the upper boundary of the forest - Caucasian Warbler, Common Rosefinch, Red Cap reel. There are representatives of the highlands - the golden eagle, black vulture, griffon vulture.
From small mammals the forest belt are common endemic Whitechest (Abkhaz) hedgehog, Caucasian mole, wood and yellow-mouse, dormouse timber etc. Because of prey, along with the usual - Bear, badger, fox, marten (wood and stone) there are also rare - European mink, otter Caucasian (rare species), Caucasian forest cat, lynx.